What is GSTR 3B – For the first two months of GST implementation, Every GST registered person have to file form GSTR 3B within the due date for each GSTN. If you have more than one GSTN, it would be required to file separate GSTR3B for each GSTN. However this form is temporary in nature, still non-filing may attract interest @18% per annum. Even, if there is no transactions or NIL tax, still every registered person have to file GSTR3B. GSTR3B contains information about summary of outward and inward supply, its tax liability.
Last date to file GSTR 3B was 25th August 2017 – The Goods and Services Tax (GST) tax was introduced on 1st of July 2017. The last date for payment of GST for the month of July 2017 was 25th August 2017. Before filing GSTR3B, first taxpayer have to deposit the GST amount through challan, which will reflect in electronic cash ledger on GST common portal. Payment of GST is complete only when amount of tax payable is debited from electronic cash / credit ledger.

Late Fee waived not Interest on late payment – Now late fee for all taxpayers who could not file GSTR 3B for the month of July 2017 has been waived, but not the interest on late payment of Tax liability.
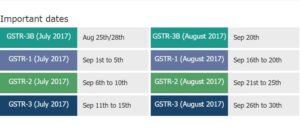
GSTR 1 is to be filed by all taxpayers by 5th of September 2017 and GSTR 2 and GSTR 3 to be filed by all taxpayers by 10th and 15th of September 2017 respectively.
Correction in GSTR3B – Taxpayers who have committed errors in GSTR 3B will be able to put the correct details in GSTR 1-2-3. However, interest will be leviable from all taxpayers who have not discharged their complete Tax liability for July 2017 by 25-08-2017.
Circular issued by Ministry of Finance in this regard – Click here for reading circular dated 01-09-2017
To,
The Principal Chief Commissioners/Chief Commissioners/Principal Commissioners/ Commissioners of Central Tax (All) The Principal Director Generals/ Director Generals (All)
Subject: System based reconciliation of information furnished in FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2 with FORM GSTR-3B – regarding
1. Sections 37, 38 and section 39 of the CGST Act, 2017(hereinafter referred to as ‘the Act’) read with rules 59, 60 and 61 of the CGST Rules, 2017(hereinafter referred to as ‘the Rules’) require every registered person to furnish details of outward supplies made in a month in FORM GSTR-1, details of inward supplies received in a month in FORM GSTR-2 and a return in FORM GSTR-3 by the 10th, 15th and 20thof the next month respectively. Keeping in view that taxpayers may face certain issues in the initial days after the introduction of GST, the GST Council extended the date for filing of FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2 for the months of July and August, 2017 and approved the filing of a simplified return in FORM GSTR-3Bfor these two months by the notified due dates after making the due payment of tax.
2. Registered persons opting to utilize transitional credit available under section 140 of the Act read with the rules made there under for discharging the tax liability for the month of July, 2017 were required to file FORM GST TRAN -1 on or before 28th August,2017. This transitional credit was to be credited to the electronic credit ledger and be available for discharging the tax liability.
3. As per the provisions of sub-rule (5) of rule 61 of the Rules, the return in FORM GSTR-3B was required to be furnished when the due dates for filing of FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2 have been extended. After the return in FORM GSTR-3B has been furnished, the process of reconciliation between the information furnished in FORM GSTR3B with that furnished in FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2 would be carried out in accordance with the provisions of sub-rule (6) of rule 61 of the Rules.
4. The detailed procedure for reconciliation of information furnished in FORM GSTR-3 and FORM GSTR-3B is detailed in succeeding paras.
Furnishing of information in FORM GSTR- 1 & FORM GSTR-2:
5. It may be noted that after the registered person has filed his return in FORM GSTR3B and the statement of outward supplies in FORM GSTR-1, the inward supplies shall be auto drafted for all registered persons (corresponding recipients of supply) and made available to them in FORM GSTR-2A as per sub-rule (3) of rule 59 of the Rules. FORM GSTR-2A is the exact replica of FORM GSTR-2 containing only those details that are autopopulated from the details furnished in FORM GSTR-1 by the corresponding suppliers. Based on the details communicated in FORM GSTR-2A, the registered person shall prepare the statement of inward supplies in FORM GSTR-2 by:-
a. adding, deleting or modifying the invoice level details communicated in FORM GSTR-2A;
b. adding information pertaining to details that are required to be furnished in GSTR-2 but are not part of FORM GSTR-2A like details of imports, details of supplies attracting reverse charge that have been received by registered person;
c. providing details of supplies received from composition suppliers and exempt, nil-rated & non GST inward supplies;
d. providing details of advances paid on inward supplies attracting reverse charge, if any, along with adjustments;
e. providing details of reversal of ITC as per the provisions of rules 37, 39, 42 and 43 of the Rules, if any; and
f. providing HSN wise summary details of inward supplies.
Correction of erroneous details furnished in FORM GSTR-3B:
6. In case the registered person intends to amend any details furnished in FORM GSTR3B, it maybe done in the FORM GSTR-1 or FORM GSTR-2, as the case may be. For example, while preparing and furnishing the details in FORM GSTR-1, if the outward supplies have been under reported or excess reported in FORM GSTR-3B, the same maybe correctly reported in the FORM GSTR-1. Similarly, if the details of inward supplies or the eligible ITC have been reported less or more than what they should have been, the same maybe reported correctly in the FORM GSTR-2. This will get reflected in the revised output tax liability or eligible ITC, as the case may be, of the registered person. The details furnished in FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2 will be auto-populated and reflected in the return in FORM GSTR-3 for that particular month.
Action on the system-based reconciliation:
7. After the registered person has furnished the statement of inward supplies in FORM GSTR-2 by the extended date, the common portal shall auto-draft Part-A of the return in FORM GSTR-3 for the said month based on the information furnished in FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2. Based on the revised figures of output tax liability and eligible input tax credit, Table 12 of Part B of FORM GSTR-3 shall be made available. The common portal would populate the correct figures of tax payable in column (2) of Table 12 of FORM GSTR3, based on the information furnished in FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2. The tax paid through the electronic cash ledger and electronic credit ledger in the return in FORM GSTR3B shall be displayed by the system in column (3) to (7) of the Table 12 of Part B of FORM GSTR-3. Where there is no difference between the details of output tax liability and eligible input tax credit furnished in FORM GSTR-3B and the details furnished in FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2, the amount of tax payable and tax paid shall be the same in FORM GSTR-3B and FORM GSTR-3. The person can sign and submit FORM GSTR-3 without any additional payment of tax.
Additional payment of taxes:
8. Where the tax payable by a registered person as per FORM GSTR-3is more than what has been paid as per FORM GSTR-3B, the common portal would show another instance of Table 12 for making additional payment of taxes, in accordance with the mandate of clause (b) of sub-rule (6) of rule 61. As the tax payable in column (2) of Table 12 of FORM GSTR-3 is more than what was shown in FORM GSTR-3B, the additional amount of tax payable can be paid by debiting the electronic cash or credit ledger as per the provisions contained in section 49 of the Act along with applicable interest on delayed payment of tax starting from 26th day of August, 2017 till the date of debit in the electronic cash or credit ledger. If the eligible ITC claimed by the person in FORM GSTR-2 is less than the ITC claimed and utilised by the registered person in FORM GSTR-3B, the same would be added to his output tax liability and shall have to be paid by him along with interest by debiting the electronic cash or credit ledger as per the provisions contained in section 49 of the Act before submitting the return in FORM GSTR-3 to complete the process. It may be noted that where the transitional credit as declared in FORM GST TRAN-1 is credited to the electronic credit ledger, the same can be utilised for the payment of the said additional tax liability.
Additional claim of eligible ITC:
9. Where the eligible ITC claimed by the taxpayer in FORM GSTR-3B is less that the ITC eligible as per the details furnished in FORM GSTR-2, the additional amount of ITC shall be credited to the electronic credit ledger of the registered person when he submits the return in FORM GSTR-3 (in accordance with clause (c) of sub-rule (6) of rule 61). However, simultaneously, if there is an increase in the output tax liability, the registered person can utilise this additional amount of ITC eligible as per the details furnished in FORM GSTR-2 along with the balance in the electronic cash ledger, if required, for the payment of the increased output tax liability and submit his return in FORM GSTR-3.
Reduction in output tax liability:
10. Where the output tax liability of the registered person as per the details furnished in FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2 is less than the output tax liability as per the details furnished in the FORM GSTR-3B and the same is not offset by a corresponding reduction in the input tax credit to which he is entitled, the excess shall be carried forward to the next month’s return to be offset against the output liability of the next month by the taxpayer when he signs and submits the return in FORM GSTR-3. However, simultaneously, if there is a decrease in the eligible input tax credit, the same will be adjusted against the above mentioned reduction in output tax liability and the balance, if any, of the reduction in output tax liability shall be carried forward to the next month’s return to be offset against the output liability of the next month.
Submission of GSTR-3B without payment of taxes:
11. Where, for some reasons, the registered person has only submitted the return in FORM GSTR-3B and has not made the payment of taxes by debiting the same from his electronic cash or credit ledger, the return shall still be subjected to the reconciliation process as detailed above. Such registered person should furnish the details in FORM GSTR-1, FORM GSTR-2 and sign and submit the return in FORM GSTR-3 along with the payment of the due taxes as per the provisions of section 49 of the Act. However, since the payment was not made on or before the due date, the registered person shall be liable for payment of interest on delayed payment of tax starting from 26th day of August, 2017 till the date of debit in the electronic cash and / or credit ledger but will not be liable to pay any late fee provided the requisite return in FORM GSTR-3B was submitted on or before the due date.
12. Where the registered person has not submitted the return in FORM GSTR-3B, he is required to furnish the details in FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2 and sign and submit the return in FORM GSTR-3 along with the payment of the due taxes as per the provisions of section 49 of the Act. However, since the payment was not made on or before the due date, the registered person shall be liable for payment of interest on delayed payment of tax starting from 26th day of August, 2017 till the date of debit in the electronic cash and / or credit ledger. No late fee, however, would be levied for late filing of return in terms of section 47 of the Act, in accordance with the recommendation of the GST Council, as notified vide Notification No. 28/2017-Central tax dated 01.09.2017.
Processing of information furnished:
13. After submission of the information in FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2, the process of matching as per section 41, 42 and 43 of the Act read with rules 69 to 76 of the Rules shall be carried out as if these details were submitted in the regular course. Any amendment in the details furnished in FORM GSTR-1 and GSTR-2 shall be done following the procedure laid down under sub-section (3) of section 37 and sub-section (5) of section 38 of the Act respectively. The return shall be considered to be a valid return when the tax payable as per FORM GSTR-3 has been paid in full after which the return shall be taken up for matching.
14. It is requested that suitable trade notices may be issued to publicize the contents of this circular.
15. Difficulty, if any, in implementation of the above instructions may please be brought to the notice of the Board. Hindi version would follow.
(Upender Gupta)
Commissioner (GST)














